
The Fourth Annual Conference of Islamic Economics & Islamic Finance
Venue: Chestnut Conference Centre; The Armoury Room; Toronto University, Canada
Date: Thursday, November 1st, 2018

ECO-ENA: Economics & ECO-Engineering Associate, Inc., Canada
ISSN: 2292-0560 = The Annual Conference of Islamic Economics & Islamic Finance
ISBN: 978-1-988081-07-6 = The Fourth Annual Conference of Islamic Economics & Islamic Finance
E-proceeding at Library & Archive Canada
Conference Type: Intellectual Symposium in a Meeting Room
Conference Reporting
Dear Conference Delegates: Thanks for making the conference successful :)
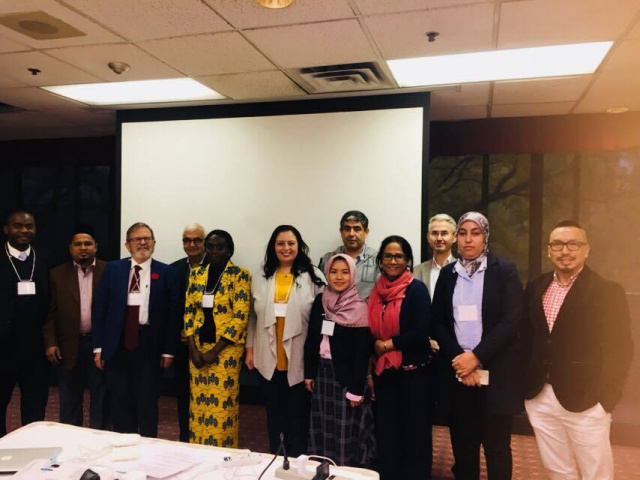

Venue: Chestnut Conference Centre; The Armoury Room; Toronto University, Toronto, Canada
Organized by: ECO-ENA: Economics & ECO-Engineering Associate, Inc., Canada
8:30 am - 9:00 am Registration & Refreshments
Program: From 8:30 a.m to 5:00 p.m
Duration/ Presentation: 30 - 40 Minutes
Session 1
From 9:00 am to 1:00 pm
Presentation (1-1)
Rodney Wilson; Professor, Durham University, UK
& International Centre for Education in Islamic Finance, Malaysia
"Risk management by Islamic banks" - Over-Skype-Presentation
Click Here for His Presentation >>>
Presentation (1-2)
Jamshid Karimov, School of Economics and Finance, Massey University, New Zealand

Paper: “Shari'ah Compliance Requirements and the Cost of Equity Capital”
Abstract:
"This study examines if adoption of Shari’ah Compliance Requirements (SCR) effects on the cost of equity capital for firms. We estimate the cost of equity capital, implied by market prices and analyst forecasts and account for changes in growth expectations around adoption of SCR. Our results show that transitional implications of Shari’ah compliance can diverge depending on information spread. The findings reveal that getting a Shari’ah compliance certificate, initially increases the cost of equity for a firm, potentially due to higher financial constraints and other burdens associated with Shari’ah requirements. However, with greater exposure and awareness in Islamic markets, Shari’ah compliance eventually leads to a fall in the cost of equity. We also find that at the industry-level, SCR adoption effects are stronger in relatively tangible sectors. Our robustness analyses confirm that becoming Sharia compliant increases the stock liquidity of SCR adopted firms, which co-varies negatively with the cost of equity."
Presentation (1-3)
Aminu Sikiru Olanrewaju, School of Management, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Malaysia

Paper: “Expanding the Waqf Horizon Through Fintech: The Industry 4.0 Wave”
Abstract:
“Fund collections for Waqf projects in some Muslim countries received some boost because of the resuscitation of the cash waqf concept. This development can improve the economic empowerment of the poor in contemporary Muslim communities given appropriate collections and effective management of the Waqf institution. Recent developments in the Financial Technology (fintech) space portend valuable relevance in the conduct and delivery of social charitable causes such as Waqf around the world. Particularly, emerging areas in FINTECH such as Islamic Crowdfunding (ICF) and blockchain have brought about greater efficiency and effectiveness through cost reduction, faster transactions, wider access, transparency and prompt disclosure of adequate information to relevant stakeholders. These FINTECH options of ICF and blockchain provide veritable opportunities to resuscitate, re-align, synergize and magnify the Islamic Social Finance (ISF) ecosystem of Waqf, Zakat and Sodaqah to generate positive and sustainable impact to the community, environment and the economy at large, with a view to projecting the Maqasid Shari’ah (Objective of the Law Giver). To document the effect of FINTECH on Waqf, this study examined the activities of six banks in Malaysia that signed a pact to utilize FINTECH for waqf collection towards improving the economy. Semi-structured Face to Face interviews were conducted with officers in charge of Waqf in the six banks, founder of the Islamic Crowdfunding platform and senior officers in Waqaf Selangor. Content analysis was used to analyze their responses, and the emergent themes were reported verbatim. Based on the derived themes, survey questionnaires were also administered to 300 customers with respect to the Waqf’s fintech functionalities of the identified banks to further confirm and strengthen the results of the interviews. Simple descriptive analysis was performed on the result of the survey questionnaire to provide clear information on the questions raised. The findings showed a disproportionate level of readiness among the banks, where few of the banks have put structure in place to increase their Waqf collections, others are at their elementary stage. However, the commitment is high across the six banks to achieve their set goals.”
Presentation (1-4)
Benjamin Geva, Professor, Osgoode Hall Law School, York University, Canada

“Pledged Land’s Harvested Produce under the Talmud’Ivan
Presentation (1-5)
Zahra Amirhosseini, Department of Financial Management, Islamic Azad University, Iran

Paper: “Effect of Financing on Liquidity Risk of the Bank in Iran”
Over-Skype Presentation >>>
Abstract:
“Banks need to control and reduce risks to continue their activity. To do this, identifying the factors affecting various risks will be very helpful. One of the most important risks associated with banking activity is liquidity risk. Considering that banks mainly finance their resources from deposits, so identifying the effective factors on liquidity risk is of particular importance. For this purpose, the aim of this study is to determine the effect of finance structure on the liquidity risk of the banks listed on Tehran stock exchange (banks financing in Iran is Islamic). In this research, the financial information of the banks accepted in Tehran Stock Exchange during the period of 2006-2017 has been investigated. To do this research, multivariate linear regression test has been used using panel data. The analysis results show that the financing structure has a significant effect on the liquidity risk of banks in Iran. The results indicate that demands deposit, saving deposit and term deposit have significant effect on the banks’ liquidity risk.”
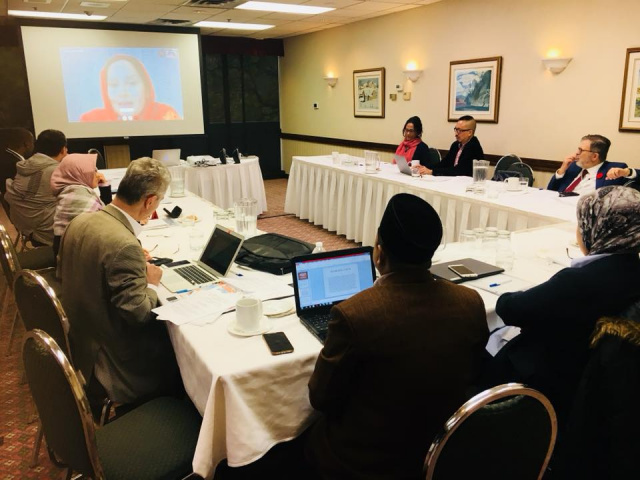
Presentation (1-6)
A panel Session chaired by Varol Senel, Avk Law Firm, Turkey

“Main Differences between the Conventional Finance and the Islamic Finance’
1:00 - 2:00 pm
(Lunch Break - All delegates are invited)
Mediterranean Vegetable Break
Session 2
From 2:00 pm to 6:00 pm
Coffee, Tea, Refreshments will be presented at 3:30 pm during the discussions.
Presentation (1-7)
Mansour Khalili Araghi , Faculty of Economics; University of Tehran, Iran

Paper: "The Role of Islamic Financial Instruments in the Iranian Economy; a Theoretical and Experimental Approach"
Abstract:
“The aim of this study is to investigate the role of Islamic financial instruments in regulating the business cycles of the Iranian economy for the period of 1994-2017. In this study structural vector autoregressive (SVAR) has been used to identify effective factors causing business cycles in the Iranian economy. The results show that the correlation coefficient between sold partnership papers and the cyclical part of the GDP in two models-with no lag and one lag in the growth rate of Partnership papers are insignificant at the 5 percent confidence interval and the null hypothesis is not rejected. However, in the model with one lag, this relation is significant at the 10 percent confidence interval and the null hypothesis is rejected. The impulse response function (IRF) show that the growth rate of real exchange rate and budget deficit are the two main factors causing the business cycles in the economy. The results reveal that the partnership papers could not be used as a policy instrument to reduce the cycles in Iran’s economy. Therefore, more studies are suggested regarding the impact of government budget deficit and how it is financed.”
Presentation (1-8)
Coulibaly Massita, Institute National Polytechnique Felix Houphouet Boigny, Cote d'lvoire

Paper: “THE DETERMINANTS OF ISLAMIC FINANCE IN WEST AFRICA: THE CASE OF COTE D’IVOIRE"
Abstract:
“Islamic finance has boomed in recent decades in both Muslim and non-Muslim countries. According to Reuter 2013, there are more than 1,000 Islamic finance institutions with combined assets of more than $ 1,300 billion (Mayada El-Zoghbi and Kaylene Alvarez 2015). In addition, many non-Muslim developed countries (Great Britain, France Luxembourg, Hong Kong, Germany, South Africa and Russia) have become increasingly interested in Islamic finance (Zamir, wordbank 2016).
However, this financial innovation, which is based on the principles of Islam, is struggling to develop in Africa, particularly in West Africa although it is the second Muslim zone of the continent. For example, the UEMOA space represents less than 0.01 percent of the Islamic finance market (Koffigan E. Adigbli 2018).
This study aims to highlight the factors that lead to the adoption of Islamic finance in Côte d'Ivoire. It helps to understand the Islamic finance services consumer’s behaviour in order to propose strategies for this sector’s development in Côte d'Ivoire.
We use the theory of diffusion of innovations and the theory of the adoption of innovations, as developed by Rogers (1983), to analyze respectively the supply side and the demand side. Our empirical analysis is based on a model of choice to adopt or not adopt Islamic products. We analyze our data through a logistics model.
Our statistical and econometric analyzes are based on survey data from 300 individuals mainly in the Abidjan, Bouaké and Yamoussoukro.”
Presentation (1-9)
Raja Daouah, University of Cadi Ayyad, Morocco & University of Basel, Switzerland
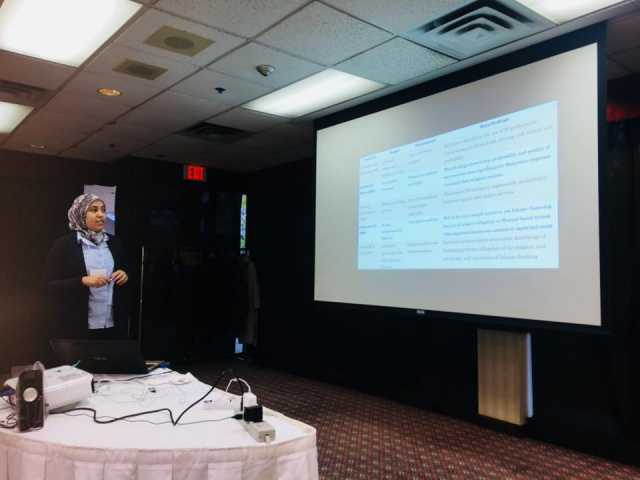

Paper: “How do Small and Medium Enterprises react to the introduction of Islamic Finance in Morocco?”
Abstract
“The purpose of this study is an empirical survey of attitudes, perception and knowledge of Islamic financial products and services by Moroccan Small and Medium Enterprises using Theory of Planned Behavior as a framework. Method: A survey research using interviewer-administered questionnaire has employed as the main approach for the data collection. INREDD Laboratory at University of Cadi Ayyad has conducted this survey in 2016. A sample of 167 Moroccan SMEs was selected using a simple random sampling technique. Descriptive analysis and logistic regression analysis were used to analyze the data collected. Results: The empirical findings based on our research framework indicate that most of SMEs are potential user of Islamic finance instruments. Noticeably, religious factors play the major role in determining the likelihood of demand of Islamic finance products by Moroccan SMEs. However, Awareness and the profit and loss sharing principle are significant factors in determining the probability of use of Islamic financial methods by SME. The findings extend our understanding of Moroccan SMEs attitudes and awareness towards Islamic finance, and they are of key importance in informing future financial industry practice and financial policy formation in Morocco.”
Presentation (1-10)
Ninik Sri Rahayu, Department of Oriental Studies, Faculty of Arts and Humanities, University of Cologne, Germany

Paper: “The Dynamic Approach of Baitul Maal Wat Tamwil (BMT) in Empowering Women: Evidence from Indonesia”
Abstract:
“This paper intends to explore the dynamic approach of Baitul Maal wat Tamwil (BMT) as the genuine model of Islamic microfinance in Indonesia to empower its clients. Albeit the BMT is not intentionally designed for women, however, the higher population of the customers are women in the micro sector. Thus, this study seeks to understand the women’s empowerment model in BMT with a particular focus on the socio-economic dimension.
By employing the qualitative method, this study selected four BMTs in Yogyakarta Special Province which represent the uniqueness of Islamic microfinance institutions in the region. The data was gathered during the fieldwork in December 2017. The data collection employs several approaches: 1) Interviews key persons including BMT managers, staff officers, and clients. 2) Reviews documents and archival of the BMT which entails BMTs annual report, leaflets and website. 3) Field observations related to the BMTs engagement in empowering their members.
This study reveals that: 1) The socio-economic intermediary process in BMTs goes through several levels depending on the socio-economic of the clients. The lower-middle income clients receive commercial financial service from the baitul tamwil (business-oriented division). Meanwhile, the very poor group get different financial treatment, in term of qard al hassan (benevolent loans) from the baitul maal (philanthropy division). 2) BMTs employ two strategies in empowering the clients: individual and collective approach. The individual approach called “jemput bola” mechanism is the most common method for BMTs to serve the clients. Jemput bola is a proactive service in which the BMT marketing officer conducts regular visits to the clients’ business site, particularly in the traditional market where the majority of women earn a living. In the collective approach, BMTs organize women’s clients into small groups. Rembug minggon (weekly meeting) and arisan (Rotating Saving and Credit Association) become an important instrument for BMTs to empower the clients collectively.
To conclude, the BMTs in Indonesia have developed a dynamic model in empowering women in micro business. As the BMTs are basically not created for women, it is necessary for BMT to accommodate women’s issue in the policy level so that the empowerment effort will significantly contribute to the women’s life.”
Presentation (1-11)
Zakir Hossain Shalim , Department of Dawah and Islamic Studies, Islamic Arabic University, Bangladesh

Paper: Islamic life insurance (Family Takaful) in Practice: A Study of Syarikat Takaful Malaysia Keluarga Berhad (STMKB)”
Abstract:
“Life insurance is an important financial tool through which the individuals can obtain financial security for their families and businesses. In order to see the application of Shari’ah principles in existing life insurance companies, this study investigates the operational policies of Syarikat Takaful Malaysia Keluarga Berhad (STMKB), a leading takaful operator in Malaysia. This study used qualitative method of data collection which includes books, articles and online recourses. This study has reached to a number of findings. Most among them are: this research affirms that though the practices of Islamic life insurance in STMKB have rendered most of the Shari’ah conditions, there are some issues which still need to be reviewed by STMKB. In order for this review, this research suggests that STMKB should mentions in its family takaful form that a nominee is the person who acts as a mere trustee to distribute the benefits among the legal heirs; STMKB should repay the surplus to the policyholders; STMKB should mention that if a person becomes an apostate whether he/she should gets takaful benefits or not; and STMKB should not take re-takaful coverage from conventional re-insurance companies.”
Presentation (1-12)
Closing with Ghada G. Mohamed; the Conference Chair.

"The Economic Management in the Cradle of Islam: Book Review"
Click Here for Her Presentation >>>
P.S. We missed those two presentations because of travel difficulties >>
Mugarura Tusiime, Financial Management, School of Accounting, Dongbei University of Finance and Economics, China
Paper: “Are Islamic stocks subject to oil price risk exposure? The Case of U.S firms”
Abstract:
“Using monthly data on a sample of Islamic stocks (listed on the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ) over the period January 1990 to December 2017, we examine using Fama- French-Carhart’s (FFC) four factor asset pricing model amplified with brent oil price factor whether oil price risk is a significant determinant of returns. The results indicate that the extent of the exposure is significantly negative using a full sample period. Moreover, results from market, size and momentum factors are highly significant whereas book-to-market has no significant impact on Islamic stock returns. We also document whether oil price risk exposures vary considerably over time. Particularly, we report robustness tests for the financial crisis of 2007–2008 and the January effect. Our results support the concept for diversification in equity investment and are thus important for investors, analysts and policy makers.”
Nirmala Moktan Gurung & Ranjit Pakhrin, Pancha Buddha Sub-Remittance Company, Nepal
Paper: “Linkages between Real Sector and Financial Sector in Nepal: A Vector Error Correction Model”
Abstract
“The financial development is considered as a pre-requisite condition for the overall economic development of the nation and rousing to economists. This paper investigates the short run and long run causality between monetary variables (M1, CPI, NFA, DC) and real sector variables (GDP, TE, TI) of Nepal using some of the econometric techniques like Johansen’s co-integration analysis and the Vector Error Correction Model (VECM). The study employs the data from 1975 to 2014. The results of the investigation aver that there exists short run and long run causality between monetary and real sector variables. The impulse responses of exports and domestic credits show that these variables have positive impacts on the economic growth which is consistent with the theoretical frameworks. The impulse responses of GDP to domestic credit seemed insignificant in the short run and started to be significant in the long run gradually. On the contrary to this, the impulse response of GDP and domestic credit to export seemed negatively responsive. So, giving proper focus on the macroeconomic policies and strategies which reduces the nebulous situations of economy and promote the allocation of resources, production activities, and competitiveness to increase the domestic credits and exports will probably promote economic development of the nation.”
Attendees >>
Could make it to the conference and significantly contributed in the discussions of the symposium:
- Anh Quan Nguyen, Thailand

- Varol Senel, Turkey (Resident in Canada)

- Rita Parvin, Canada (Invited to attend)

Couldn't make it to the conference because of travel difficulties:
- Abulizi Abudureheman, KSA
- Amer Omer, Sudan
- Ola Eltigani, Sudan
- Elmoiz Ismail Mahmoud Ismail, Sudan
- Osama Mohamed Abdalla Elhassan, Sudan
- Mohammed Hassan Mohamed Youssif, Sudan
- Taj-Alsir Ahmed Mohamed, Sudan
- Namirembe Agnes, Uganda
- Fatemeh Fakhari, Iran
- Ribenson Bonhomme, Haiti
- Elie Michee Kemgang Nana, Cameroon
- Ssemwogerere Charles, Uganda
- Nakato Haawa, Uganda
- Abdulmalik Sadiq, Germany
- Felix Maditka Panzu, The Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Jadalhak Adam, Ghana
All rights reserved
ECO-ENA: Economics & ECO-Engineering Associate, Inc.®
Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
research_forum@eco-ena.ca
www.eco-ena.ca